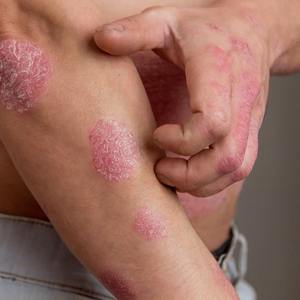
Eczema, medically known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition that affects millions worldwide. This inflammatory disorder causes the skin to become red, itchy, and irritated. Eczema can appear at any age, though it is commonly seen in children. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatments can help those affected manage their condition more effectively and improve their quality of life.
What Is Eczema?
Eczema is characterized by patches of skin that become dry, cracked, itchy, and inflamed. These areas are often found on the face, neck, hands, and inside the elbows and knees, but they can develop anywhere on the body. The areas commonly affected include:
Upper Chest and Back: Less common but possible, especially in severe cases.
Face and Scalp: Especially in infants, who often develop “cradle cap.”
Hands and Feet: Areas prone to frequent washing or exposure to irritants.
Inside the Elbows and Knees: Common in children and adults, these areas are vulnerable to flare-ups.
Wrists and Ankles: Another frequent site, particularly in children.
Common Symptoms
The symptoms can vary from mild to severe and may flare up periodically.
Typical symptoms include:
- Dry, scaly skin: The skin may feel rough and appear flaky.
- Itching: This is often intense and worsens at night, leading to scratching and further irritation.
- Red or brown patches: These can appear anywhere, but are common on hands, feet, and behind the knees.
- Thickened, cracked skin: Over time, chronic scratching can cause the skin to thicken.
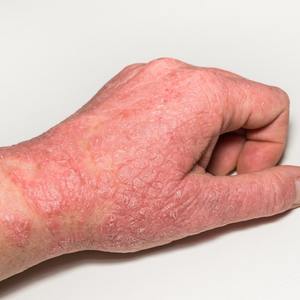
Causes and Triggers
The exact cause of eczema remains unknown, but experts believe a combination of genetic and environmental factors is involved. A malfunction in the skin barrier—responsible for retaining moisture and protecting against irritants—makes individuals with eczema more prone to dryness and infection. Other contributing factors include:
- Genetics: Often runs in families, suggesting a hereditary link.
- Immune System Response: Eczema is thought to be an overactive immune response to triggers.
- Environmental Irritants: Soaps, detergents, dust, pet dander, and certain fabrics can worsen symptoms.
- Climate and Weather: Cold, dry air and high humidity can exacerbate eczema.
- Stress: Emotional stress can trigger flare-ups, as the body releases hormones that may worsen skin inflammation.
- Diet: In some cases, food allergies or sensitivities (like to dairy, eggs, or nuts) can contribute to symptoms, especially in children.
Treatment Options
Managing eczema typically involves a combination of lifestyle adjustments, skincare routines, and medications. Some effective treatments include:
- Moisturizers: Regular application of hypoallergenic moisturizers helps keep the skin hydrated, reducing dryness and irritation.
- Topical corticosteroids: These anti-inflammatory creams help control itching and inflammation during flare-ups.
- Medicated creams: Non-steroidal creams, such as calcineurin inhibitors, can be used as an alternative to steroids.
- Phototherapy: Exposing the skin to controlled amounts of UV light has been shown to help reduce symptoms in some people.
Lifestyle Adjustments and Prevention Tips
Managing eczema involves lifestyle adjustments to avoid triggers and keep the skin barrier healthy. Some tips include:
- Dietary Awareness: For those with food triggers, eliminating problem foods may alleviate symptoms, but dietary changes should be supervised by a healthcare professional.
- Gentle Skincare Routine: Use fragrance-free, gentle cleansers, and avoid hot showers, as these can strip moisture from the skin.
- Moisturize Regularly: Apply a thick, non-fragrant moisturizer multiple times daily to lock in hydration.
- Wear Soft, Breathable Fabrics: Cotton is generally a safe choice, while wool and synthetic fabrics may cause irritation.
- Manage Stress: Techniques like mindfulness, exercise, and deep breathing can reduce stress-related flare-ups.
Living with Eczema
Living with eczema can be challenging, but many people manage symptoms well with the right treatment and preventive care. Consulting a dermatologist is important for creating a personalized treatment plan, especially for severe cases. With continued research, new therapies continue to emerge, providing hope and better control for those affected by eczema. By implementing a well-rounded approach to treatment and self-care, people with eczema can enjoy a more comfortable and fulfilling life.